When we think of mortgages, we generally assume this loan is for buying or building a new home, but a mortgage can also be used to renovate, repair or restore a home. Regardless of your situation, there is a loan out there that is right for you.
So how do you choose the right mortgage for you? What exactly are the different loan types? To find the right mortgage loan for your situation, you should understand all of your options to be sure you’re getting the ideal loan for you. If you’re looking for an explanation of the different types of mortgage loans, we’re here to help.
Table of Contents
- Different Types of Mortgage Loans Explained
- FHA
- USDA
- Construction
- VA
- Jumbo
- Conventional
- Fixed-Rate
- Adjustable-Rate
- Reverse
- Balloon
- Second Mortgages
- Finance With Assurance Financials
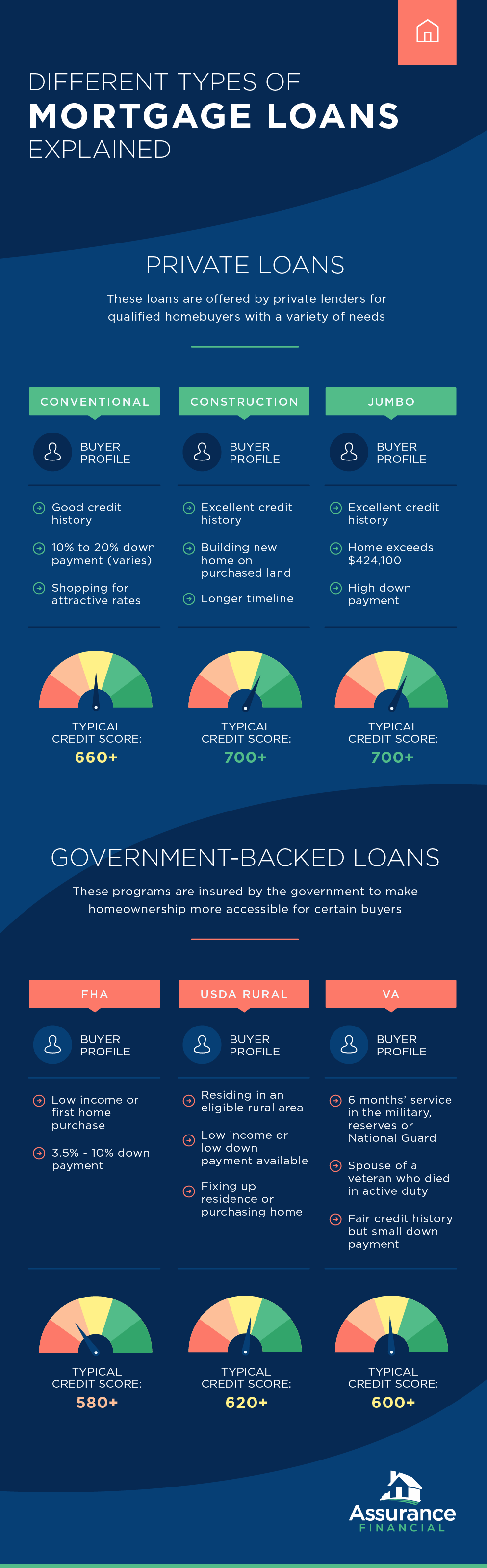
Different Types of Mortgage Loans Explained
In real estate, there are several types of mortgage loans and interest rates. Consider the following mortgages and interest rates to determine what options might be the best for you:
1. FHA
The first kind of loan we’ll discuss is the FHA loan.
What Is an FHA Mortgage Loan?
FHA stands for Federal Housing Administration. These mortgages are backed by the government and insured by the FHA.
Who Should Apply for an FHA Loan?
FHA mortgage loans are a common option for those with less-than-excellent credit and low income. They are also popular with borrowers buying their first home. Borrowers who want a fixed-rate mortgage can get an FHA loan with a fixed rate of 15 or 30 years. Repeat buyers can also get an FHA loan, provided they use the loan for purchasing a primary residence.
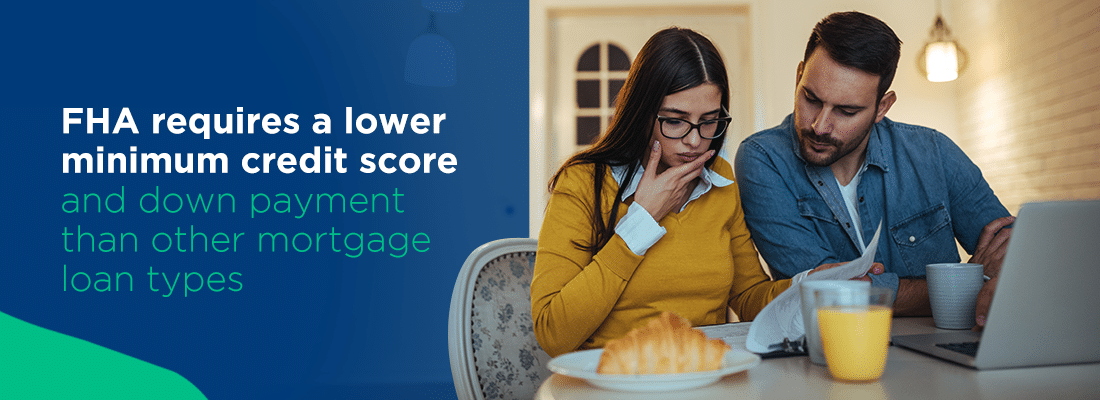
What Are the Requirements for Receiving an FHA Loan?
FHA requires a lower minimum credit score and down payment than other mortgage loan types. However, borrowers of an FHA loan must pay FHA mortgage insurance to protect the lender if they default on their loan. Though most borrowers must pay mortgage insurance when they put less than 20% down, all borrowers of FHA loans must pay two types of insurance premiums — an annual premium and an upfront premium.
- Annual insurance premium: Depending on the loan term, loan amount and the loan-to-value ratio, this mortgage insurance premium can range from 0.45% up to 1.05% of the total loan amount. The amount of this premium is divided by 12 for every month of the year and paid each month.
- Upfront insurance premium: This premium is 1.75% of the total loan amount and is paid once the borrower acquires their loan. The amount of the premium can be included in the financed mortgage loan amount.
Are you eligible for an FHA loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you:
- You have a FICO credit score in the range of 500 to 579 with a down payment of at least 10%.
- You have a FICO credit score of at least 580 with a down payment of at least 3.5%.
- You’ve been employed for the past two years.
- You can verify your income with pay stubs, bank statements and tax returns.
- Your FHA loan will be used for your primary residence.
- Your property is appraised and meets property guidelines.
- Your monthly mortgage payments won’t be more than 31% of your monthly income. Some lenders may allow up to 40%.
What Is the Approval Process for an FHA Loan?
The application process is intentionally designed to be flexible to increase the number of buyers entering the housing market. Closing costs for FHA lenders are limited to no more than 5% of the total loan amount.
2. USDA
A more uncommon type of mortgage loan is the USDA loan.
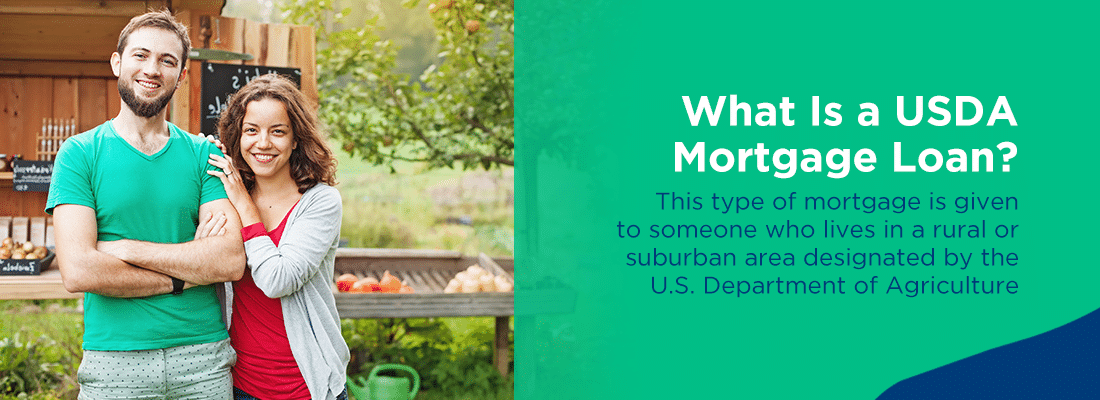
What Is a USDA Mortgage Loan?
This type of mortgage is given to someone who lives in a rural or suburban area designated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Borrowers must also live in the house the loan is for.
Who Should Apply for a USDA Loan?
Unlike many other loans where your credit and income are considered the most important factors, the most significant factor for this type of mortgage is the location of your home. Those who live in an eligible area can apply for this loan. These loans are great for applicants with low to moderate levels of income and those who are seeking a loan for home improvements.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a USDA Loan?
USDA mortgage loans generally have low interest rates with zero down payment, so the barriers for receiving this loan are relatively low. You must have a decent credit history, but an excellent credit score isn’t necessary to qualify.
Are you eligible for a USDA loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you:
- You have a relatively low income in your area. You can check the USDA’s page on income eligibility to determine whether you qualify.
- You’ll be making the home your primary residence, or for a repair loan, you occupy the home.
- You must be able to verify that you’re able and willing to meet the credit obligations.
- You must either be a U.S. citizen or meet the eligibility requirements for a noncitizen.
- You must be purchasing an eligible property.
What Is the Approval Process for a USDA Loan?
To get approved for USDA loan, you don’t need a down payment and you don’t need to be a first-time homebuyer. Additionally, the seller can contribute to your closing costs.
3. Construction
If you want to build a house, you’ll likely need a construction loan.
What Is a Construction Mortgage Loan?
This type of mortgage loan involves buying land on which to build a house. These loans typically come with much shorter terms than other loans, at a maximum term of one year. Rather than the borrower receiving the loan all at once, the lender will pay out the money as the work on the home construction progresses. Rates are also higher for this mortgage loan type than for others.
There are two types of construction loans — construction-to-permanent loans and construction-only loans.
- A construction-to-permanent loan is essentially a two-in-one mortgage loan. This is also known as a combination loan, which is a loan for two separate mortgages given to a borrower from a single lender. The construction loan is for the building of the home, and once the construction is completed, the loan is then converted to a permanent mortgage with a 15-year or 30-year term. During the construction phase, the borrower will pay only the interest of the loan. This is known as an interest-only mortgage. During the permanent mortgage, the borrower will pay both principal and interest at a fixed or variable rate. This is when payments increase significantly.
- A construction-only loan is taken out only for the construction of the house, and the borrower takes out another mortgage loan when they move in. This may be a great option for those who already have a home, but are planning to sell it after moving into the home they’re building. However, borrowers will also pay more in fees with two separate loans and risk running the chance of not being able to move into their new home if their financial situation worsens and they can no longer qualify for that second mortgage.
Who Should Apply for a Construction Loan?
Borrowers looking to buy land on which to build a home should apply for this type of loan. A construction loan can be used to cover the expenses of the work and materials, including permits, labor, framing costs and finishing costs.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a Construction Loan?
Construction mortgages are one of the most difficult to secure and thus also one of the most uncommon. This is because with other loans, in the event that the borrower defaults on their loan payments, the bank can then seize the home. In these cases, the home is collateral. However, with a construction loan, this isn’t an option, which makes the mortgage riskier for the bank.
The requirements for receiving this loan are a large down payment, a good to excellent credit score, a stable income and a low ratio of debt-to-income. You’ll also need savings for any extra expenses you encounter along the way during the construction of the home.
What Is the Approval Process for a Construction Loan?
To get approval for a construction loan, the borrower will need to submit to the lender a construction timetable with a realistic budget and detailed plans. Borrowers generally only need to make interest payments while construction is in progress. The lender typically sends someone to verify the home’s construction progress whenever the borrower requests funds.
4. VA
If you are a veteran, you might be eligible for a VA mortgage loan.
What Is a VA Mortgage Loan?
VA stands for Veterans Affairs. These mortgages are obtained through a lender but backed in part by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Though there aren’t any limits on the amount of a borrower’s loan, there are limitations on how much will be guaranteed by the VA.
These loans generally have lower rates than other mortgage loans. Borrowers can use their VA loan only for a primary residence, so they cannot be used for vacation homes or investment properties. VA loan holders are also not required to pay private mortgage insurance. Following six months of active duty, this mortgage type is provided with 100% financing.
Who Should Apply for a VA Loan?
VA mortgage loans can be given to members of the national guard, reserves, military or spouses of service members who died during active duty. These mortgage loans don’t require a down payment or excellent credit, so this can be an excellent option for those without much saved up for a down payment or without great credit.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a VA Loan?
Are you eligible for a VA loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you. You may qualify for a VA loan if:
- For 90 consecutive days, you served in active service during a time of war.
- For 181 days, you served in active service during a time of peace.
- For 6 years, you have been an active member of the Reserves or National Guard.
- You are the spouse of a service member who died during active service or from a disability related to their service.
You’ll also need to meet your lender’s requirements of credit score, debt-to-income ratio and income.
What Is the Approval Process for a VA Loan?
First, borrowers will need to apply for a Certificate of Eligibility. They can request this from the lender, apply through VA.gov or mail in their application form. After obtaining their COE, borrowers can then apply for their VA loan through their lender.
5. Jumbo
Another uncommon type of mortgage is the jumbo loan.
What Is a Jumbo Mortgage Loan?
Jumbo mortgages are based on the price of the home. Homes exceeding $424,100 fall into this mortgage bracket. Though historically, jumbo loans have carried higher interests than other mortgage loans, jumbo mortgage interest rates are now closer to the rates of other loan types.
Who Should Apply for a Jumbo Loan?
High-income earners making between $250,000 and $500,000 annually and who are looking to buy high-cost homes in a competitive local market or luxury homes are generally the borrowers who should apply for a jumbo mortgage.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a Jumbo Loan?
Jumbo loans are risky for lenders because of their large amount and lack of guarantee by the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae) or the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (Freddie Mac), so eligibility requirements of borrowers are more demanding. To qualify for a jumbo mortgage, you’ll need an excellent credit score of above 700, a large down payment and a low debt-to-income ratio, preferably close to 36%. Interest rates can be high but are also tax deductible.
What Is the Approval Process for a Jumbo Loan?
To get approved for a Jumbo loan, you’ll need to prove you have reserves of cash and provide W2 tax forms for two years and 30 days of pay stubs.
6. Conventional
The most common type of mortgage is the conventional loan.
What Is a Conventional Mortgage Loan?
Finally, the most common mortgage type is the conventional mortgage, representing about two-thirds of loans issued to homeowners in the US. This loan is essentially any type of mortgage that isn’t offered by a government entity such as the FHA, VA or USDA Rural Housing Service. Instead, this type of loan is available through Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. The down payment tends to be a bit higher than other mortgages, and it also offers two interest rate options — fixed and adjustable.
Who Should Apply for a Conventional Loan?
Conventional mortgages can be a great option for both new homebuyers and existing homeowners. Though interest rates tend to be higher than for government-backed loans, insurance premiums required by other loan types may result in the same total cost over the long term.
This mortgage loan type is also generally the best loan option for those who want to buy a second home, a home to use as an investment property or a home valued over $500,000.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a Conventional Loan?
Are you eligible for a conventional loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you:
- Your credit score is at least 680. A higher score can potentially result in a lower interest rate, especially for those with a score over 740.
- You have a reasonable or low debt-to-income ratio. The ratio of your financial obligations to your monthly income should be around 36% and should not exceed 43%.
- You have saved up enough for a down payment of 20%. Though a smaller percentage can be accepted, borrowers usually are then required to pay for private mortgage insurance.
What Is the Approval Process for a Conventional Loan?
To get approved for a conventional mortgage loan, borrowers need to complete an official application and supply their lender with any necessary documents for the lender to check their background, credit score and credit history. Lenders look for borrowers who can afford their monthly mortgage payments –– payments that typically should be 28% or less of their gross income –– can afford a down payment and can afford other upfront expenses, such as fees and closing costs.
7. Fixed-Rate
Fixed-rate mortgages come with a rate that doesn’t change during the loan’s duration. Though the amount of the principal and interest that are paid every month varies, the monthly payment stays consistent, making budgeting easier and more predictable for homeowners.
A fixed-rate mortgage protects homeowners from increases in interest rates in the housing market, but they can also be higher in comparison to variable rates. This rate can be possible for multiple term options, such as 30, 20 or 15 years.
8. Adjustable-Rate
The opposite of fixed-rate mortgages are adjustable-rate mortgages, which have variable rates. This means the rate of the mortgage can vary from year to year and are generally more complicated than mortgages with fixed rates.
The rate adjusts on an established set of time, generally every one, three or five years. If your adjustment occurs every five years, this means your monthly payments will be consistent for the first five years of your loan. After those five years, your interest rate will adjust and your payments will either increase or decrease.
9. Reverse
A reverse mortgage is a loan for a homeowner 62 years of age or older who wants to borrow against their home’s value. The homeowner doesn’t have to make loan payments, and they’ll receive their loan in the form of a lump sum, line of credit or monthly payment. The loan balance will become due when the borrower permanently moves away, sells their home or dies. The loan amount won’t exceed the value of the home, and the borrower will also not be responsible for paying more should their home’s value decrease.
These loans are an option for homeowners age 62 or older who have most of their net worth tied up in their home and need cash.
10. Balloon
A balloon mortgage is a loan in which the borrower repays in the form of a lump sum. This type of loan is typically short-term but can be held for as long as 30 years, they can have variable or fixed rates and they may require interest-only monthly payments. Balloon loans also generally offer higher interest rates due to the increased risk for lenders.
11. Second mortgages
Second mortgages are taken out after a borrower’s first mortgage and are generally used for financing home improvements, consolidating debt or for covering enough of the first mortgage to avoid the requirement of paying the mortgage insurance. Second mortgages generally have terms that last only up to 20 years and can be as short as one year.
[download_section]
Financing Your Mortgage With Assurance Financial
Financing your mortgage should be an exciting time in your life, and at Assurance Financial, we strive to help you make it a time that is as memorable and simple as possible. You should be able to enjoy this step in your journey toward homeownership while someone else handles the heavy lifting. That’s where we come in.
We’re an independent lender, and we want to make your dreams of homeownership a reality. We offer end-to-end processing all under one roof so that your path to owning your dream home is a smooth and fast one.
Find a loan officer with us today and let us help you secure the mortgage terms of your dreams for the home of your dreams.