Category: FHA
Potential homebuyers, especially first-time homebuyers, often wonder how much money they should save to purchase a home. There are a number of costs associated with the process, including a down payment and closing costs. Fortunately, 100% financing options are available for home loans that may allow you to purchase a home with no money down. If you are looking for a home loan with 100% financing, meaning a home loan that doesn’t require a down payment, we cover what you need to know.
What Is a 100% Financing Home Loan?
A 100% financing home loan is a type of mortgage loan that allows you to finance the entire purchase price of a home without making a down payment. With this type of loan, you don’t need to put any money down, which can make it easier for you to purchase a home if you do not have a large amount of savings or want to keep your savings for other purposes.
There are a few different types of 100% financing home loans available, including United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) loans and Veterans Affairs (VA) loans. These loans are backed by the government and are designed to help make homeownership more affordable and accessible to a wider range of people.
While a 100% financing home loan may appeal to some borrowers, this option may also come with higher interest rates and fees. Carefully consider your options and work with a reputable lender to ensure you are getting the fairest loan terms possible.
What Options Are Available for No Money Down Home Loans?
There are two government-backed home loan options that do not require a down payment — a USDA loan and a VA loan.
USDA Home Loan
This type of mortgage loan is guaranteed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). A USDA home loan is designed to help low- to moderate-income borrowers in rural areas purchase a home or make home repairs. USDA loans typically offer favorable terms, including low-interest rates and zero down payment requirements. They are also available to borrowers with lower credit scores than other types of loans.
To qualify for a USDA loan, the property you plan to purchase or renovate may need to be located in a designated rural or suburban area as defined by the USDA. Additionally, you may need to meet certain income limits based on the area you are buying in and your household size. USDA loans are administered by approved lenders, and since the USDA guarantees these loans, lenders are protected from losses if you default on your loan.
VA Home Loan
This type of mortgage loan is guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). A VA loan is designed to help current and former members of the U.S. military and their qualifying surviving spouses buy or refinance a home. VA loans typically offer favorable terms, such as no down payment requirement and no private mortgage insurance requirements, making them an attractive option for eligible borrowers.
To qualify for a VA loan, you may need to obtain a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) from the VA. The COE verifies that you meet the VA’s service requirements and are eligible for the loan. Like USDA loans, VA loans are administered by approved lenders, and the guarantee from the VA protects lenders from losses if you default on the loan.
Benefits of 100% Financing for Home Loans
Receiving 100% financing for home loans, also known as zero-down payment loans, can offer you several benefits. The following are some of the potential benefits:
- Increased flexibility: If you have saved up a down payment, you can use these funds for other expenses, such as home renovations, moving costs or emergency expenses.
- No down payment required: With 100% financing, you are not required to come up with a large down payment to purchase a home, which can be a significant financial burden.
- Faster path to homeownership: With 100% financing, you can achieve your dream of homeownership sooner.
- Affordable monthly payments: With no down payment, the loan amount is higher, but the monthly payments may still be manageable, especially with competitive interest rates.
100% financing may not be available for all types of home loans, and we recommend that you carefully consider the terms and conditions of any loan before making a decision. Additionally, you may be required to have strong credit scores and income to qualify for this type of loan.
How to Buy a House With No Money Down
Buying a house with no money down is possible, but it may require careful planning and a good understanding of your options. The following are some potential ways you can buy a house with no money down:
- Gift funds: If you have friends or family who are willing to help you purchase a home, they can give you a monetary gift that you can use as a down payment.
- Negotiate with the seller: In some cases, you may be able to negotiate with the seller to cover some or all of the down payment as part of the sale agreement.
- Apply for a VA loan or USDA loan: If you are a current or former member of the U.S. military or a qualifying surviving spouse, you may be eligible for a VA loan, which requires no down payment. If you are looking to buy a home in a rural area, you may be eligible for a USDA loan, which also requires no down payment.
- Down payment assistance programs: Some state and local governments offer down payment assistance programs to help you buy a home with little or no down payment if you are a low- to moderate-income earner.
Keep in mind that even if you are able to buy a house with no money down, you may still be responsible for other costs associated with the home purchase, such as closing costs and appraisal fees. Carefully consider all of your options and speak with a qualified mortgage professional to help you navigate the homebuying process.
What if I Don’t Qualify for 100% Financing for a Home Loan?
If you don’t qualify for 100% financing for a home loan, you may have some other options, such as applying for a conventional loan, applying for an FHA loan, applying for down payment assistance, applying for closing cost assistance or saving for a down payment.
Apply for a Conventional Loan
This type of mortgage loan is not guaranteed or insured by a government agency like the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) or the Federal Housing Administration (FHA). Conventional loans are backed instead by private lenders and investors. Typically, conventional loans come with stricter credit and income requirements than government-backed loans. They are often a good option for borrowers who have good credit scores and sufficient income to qualify for a loan.
Conventional loans can be conforming or nonconforming. Conforming loans are those that meet the guidelines set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, the two government-sponsored enterprises that buy and sell mortgage loans. Nonconforming loans, also known as jumbo loans, exceed the conforming loan limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
Conventional loans typically require a down payment of at least 3% of the purchase price, although some lenders may want a larger down payment depending on your credit score and other factors. You may also be required to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI) if you make a down payment of less than 20%. Conventional loans are a popular option for homebuyers who meet the credit and income requirements and want to avoid the mortgage insurance requirements of government-backed loans.
Apply for an FHA Loan
This type of mortgage loan is backed by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), a government agency that belongs to the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). An FHA loan is designed to help lower-income and first-time homebuyers who may have difficulty qualifying for a conventional mortgage loan. The FHA insures the loan, which means that if you default on the loan, the lender is protected against losses.
FHA loans typically have more lenient credit and income requirements than conventional loans, and they may require a lower down payment. The down payment for an FHA loan can be as low as 3.5% of the purchase price, although you may be required to make a down payment of at least 10% if your credit score is lower than 580.
One of the key benefits of an FHA loan is that it allows you to qualify for a loan with a lower credit score than would typically be required for a conventional loan. Additionally, FHA loans may offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment terms than conventional loans. However, FHA loans may also require you to pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP), as well as an annual MIP that is added to the monthly mortgage payment. The MIP is used to fund the FHA loan program and protect lenders against losses.
Apply for Down Payment Assistance
Down payment assistance (DPA) is a type of financial assistance that is designed to help homebuyers cover the upfront costs associated with purchasing a home, specifically the down payment and closing costs. Down payment assistance programs are often administered by state and local housing agencies and nonprofit organizations.
Down payment assistance can take many forms, such as grants, loans or forgivable loans. The funds can be used to cover all or a portion of the down payment and closing costs, depending on the program’s guidelines and your qualifications. DPA programs are typically targeted at low-income homebuyers and first-time homebuyers who may struggle to save for a down payment. They can also be available to certain groups, such as first-time homebuyers, veterans or teachers.
The goal of down payment assistance is to make homeownership more accessible and affordable to a wider range of people. By reducing the upfront costs of buying a home, DPA programs can help you get into a home faster and with less financial strain. Down payment assistance programs may have specific requirements and qualifications that you may need to meet to be eligible. Carefully review the guidelines of any DPA program you are considering to ensure that you meet the qualifications and understand the terms of the assistance.
Apply for Closing Cost Assistance
Closing cost assistance is a type of financial assistance that can help you cover the closing costs associated with purchasing a home. Closing costs are expenses that are incurred during the homebuying process, such as lender fees, appraisal fees and title fees. Closing cost assistance programs are often administered by state and local housing agencies and nonprofit organizations. The assistance can be used to cover some or all of the closing costs.
Closing cost assistance is typically targeted at low- to moderate-income homebuyers who may struggle to cover the upfront costs of buying a home to make homeownership more accessible and affordable. Check if there are any closing cost assistance programs available in your area.
Save for a Down Payment
Trying to save for a down payment on a home can be a significant challenge, especially if you’re starting from scratch. However, there are several strategies that can help you save money more effectively and reach your down payment goal faster, such as:
- Reduce debt: Pay off high-interest debt, such as credit cards, as quickly as possible. This will free up more money for savings.
- Create a budget: Make a budget that takes into account your income and expenses and look for areas where you can cut back on spending. Consider reducing discretionary expenses like eating out, entertainment and subscriptions.
- Set a savings goal: Determine how much you need to save for a down payment and set a specific savings goal. This will help you track your progress and stay motivated.
- Consider a side hustle: Look for ways to earn extra income, such as freelancing, tutoring or selling items you no longer need. Put this extra income directly into your down payment savings account.
- Automate your savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to a savings account each month. This will help you save money consistently and avoid the temptation to spend it elsewhere.
Saving for a down payment can take time and discipline, but if you don’t qualify for 100% financing, this can be an important step toward achieving homeownership.
Where to Start
Every homebuyer has different needs, which is why we offer so many different home loan options at Assurance Financial. We can help regardless of your life stage or homebuying goal, whether you are:
- First-time homebuyers.
- Vacation homebuyers.
- Experienced homebuyers.
- Self-employed homebuyers.
We can also assist if you’re downsizing your home, remodeling or building a home, or investing in real estate. Use a 100% financing mortgage calculator to determine how this mortgage may impact your finances.
Apply for a Loan Today With Assurance Financial
At Assurance Financial, we have been servicing the loan industry since 2001. We combine superior customer service with technology-focused solutions to bring you the most seamless homebuying experience possible. We handle the entire home loan process in-house, so you can rest assured that the process will go smoothly. If you are seeking 100% financing for a conventional loan or another type of home loan, apply for a loan with us at Assurance Financial today.
Not every potential homeowner qualifies for a conventional mortgage — and that’s okay. Several mortgage programs exist that help people buy a home, even if their credit isn’t the best or even if they don’t have a large down payment saved up. If you are hoping to buy a home soon, but aren’t sure that you’ll qualify for a conventional mortgage, it can be worthwhile to look at government-backed home loan options, such as a VA loan or FHA loan.
While both have less-strict requirements for borrowers compared to conventional loans, there are some differences between FHA and VA loans. Some people might qualify for an FHA loan, but not a VA loan, for example. Another notable difference between a VA loan and an FHA loan is the size of the down payment. In this guide, we’ll discuss what’s required of each, so you can determine which one might be right for you.
Table of Contents
- FHA Loan Requirements
- VA Loan Requirements
- Similarities and Differences
- Which is Right for You?
- Find Out if You Qualify Today
FHA Loan Requirements
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loan program has been around since 1934. Its goal is to help as many people as possible buy a home. Under the program, mortgages are made by the same lenders and banks who issue conventional mortgages. Unlike conventional mortgages, the amount of an FHA loan is backed or insured by the government.
If the borrower stops making payments, the FHA will step in. Since the government insures the loan, lenders can feel comfortable offering mortgages to people who don’t have excellent or very good credit. Lenders can also offer a relatively favorable interest rate to an FHA borrower, even if the borrower isn’t making a large down payment or doesn’t have the best credit.
FHA loans aren’t available to everyone, though. A borrower does need to meet a few requirements before they can get approved from an FHA mortgage. For example, they need to have a credit score of at least 500. The down payment on an FHA loan can be as little as 3.5 percent of the price of the home, but to put down less than 10 percent, a person’s credit needs to be at least 580.
Another notable requirement of an FHA loan is mortgage insurance. While the government’s guarantee does make mortgages possible for more people, the guarantee isn’t free. Borrowers need to pay mortgage insurance on the loan, in addition to the principal and interest. FHA mortgage insurance comes in two forms.
The first is an upfront payment of 1.75 percent of the loan’s value. The second is an ongoing monthly payment ranging from 0.45 to 1.05 percent of the value of the loan. The amount of the monthly payment depends on the size of the down payment and the length of the loan.
The monthly mortgage insurance premium would be for the entire length of the FHA loan unless the down payment was 10 percent or higher. If a borrower puts down more than 10 percent of the value of the home, they will need to pay a mortgage insurance premium for 11 years.
VA Loan Requirements
Like the FHA loan program, the VA loan program is a government-insured mortgage program. Also, like FHA loans, VA loans are made by private lenders and banks. However, in the case of VA loans, The Department of Veterans Affairs backs or insures the loans. VA loans have lower down payment requirements compared to conventional mortgages and FHA loans. In some cases, an eligible borrower can get a VA loan without a down payment. About 90 percent of VA-backed loans are issued without the borrower making a down payment.
There isn’t a published minimum credit score that a person needs to have to be eligible for a VA loan. Instead, a lender typically reviews applications for VA loans on a case-by-case basis.
The most notable requirement of VA loans is that the person is either a veteran or active-duty service member or a member of the National Guard or Reserve. How long a person needs to have served varies based on when they served or if they are currently on active duty. In some cases, the length of service requirement doesn’t need to be met if a person was discharged for a qualified reason. Surviving spouses or spouses of prisoners-of-war or veterans who are missing in action might also be able to qualify for a VA loan.
To prove eligibility, a veteran or active duty service member needs to apply for a certificate of eligibility.
VA Loan Versus FHA Loan: Similarities and Differences
If you’re shopping for a mortgage, it can be helpful to take a close look at how FHA loans compare to VA loans. If you’re eligible for both, understanding the differences between the two can help you narrow down your home loan options.
1. Eligibility
The most important difference between a VA loan and an FHA loan is eligibility. You can only get a VA loan if you are currently or have been a member of the armed forces or if you’re a surviving spouse of a veteran or POW. You also need to meet the length-of-service requirements.
FHA loans aren’t restricted to a certain type of person or a certain group of people. You do need to have a Social Security number to be eligible for an FHA loan.
2. Type of Home
For both an FHA loan and a VA-backed loan, the home you purchase needs to be the home you’ll live in as your primary residence. You can’t use either loan to buy a vacation property or investment property.
You can use an FHA loan or VA loan to purchase a home with one to four units.
One common misconception about both FHA and VA loans is that they are only for first-time homebuyers. While both types of mortgages can be a great choice for a first-time buyer, there are no rules that restrict the loans to first-timers only.
3. Minimum Credit Score
One difference between FHA and VA loans is the credit score required. For an FHA loan, you need to have a credit score of at least 500. If your score is between 500 and 579, you’ll have to put down 10 percent to qualify for the mortgage. If your score is at least 580, your down payment can be as low as 3.5 percent.
The VA loan program doesn’t have a minimum score requirement. It encourages lenders to look at the full picture, including a borrower’s credit history, employment history and assets, when making a decision.
4. Maximum Loan Amount
The VA and FHA loan programs have different maximum amounts. The VA loan limit is the same as the limit for conforming conventional mortgages. The exact amount of the limit varies based on the number of units in the home and the location of the property. Homes in areas with a higher cost of living have higher mortgage limits compared to homes in areas with a lower cost of living.
Borrowers who qualify for a VA-backed loan are eligible for an entitlement, which is the amount the VA will pay to a lender if a borrower ends up defaulting on the loan. The VA has two types of entitlement:
- Basic entitlement: The basic entitlement is the lesser of $36,000 or 25 percent of the loan’s principal. Usually, a lender will lend up to four times the amount of the basic entitlement without requiring a down payment.
- Bonus entitlement: The bonus entitlement is based on the conforming loan limits for conventional loans. The VA will guarantee 25 percent of the conforming limit for your area with the bonus entitlement.
Although VA entitlement limits how much the VA insures, it doesn’t necessarily restrict how much you can borrow. If you have the means to make a down payment, you might be able to borrow more or buy a more expensive home.
The maximum amount of an FHA loan is based on the location and size of the home. A one-unit home in an area with an average cost of living can cost up to $331,760. A one-unit home in an area with a high cost of living can cost up to $765,600.
5. Minimum Down Payment
One of the features of the VA-back loan program that makes it so appealing to eligible borrowers is that often, a down payment isn’t required. The minimum down payment for an FHA loan is 3.5 percent.
6. Maximum Debt-To-Income Ratio
The debt-to-income ratio compares the amount of your monthly debt to the amount of your monthly income. You can calculate it by dividing your total monthly debt payments to your total monthly income. For example, if you pay $1,000 toward a credit card and student loan payment each month and you earn $4,000 a month, your debt-to-income ratio is 25 percent:
1,000/4,000 = 0.25 (25%)
When deciding to approve or deny a mortgage application, a lender will look at your total debt-to-income ratio to see if the amount you want to borrow will be too much of a burden or too challenging for you to pay.
For most mortgages, including an FHA loan, the maximum debt-to-income ratio is 43 percent. There are some exceptions, though, and some lenders might accept a borrower with a debt-to-income ratio as high as 50 percent.
VA loans don’t have a maximum debt-to-income ratio, but a ratio of 41 percent or lower is often preferred.
The lower your debt-to-income ratio, the more comfortable you’re likely to be making your mortgage payments and affording other expenses. Although you can go up to 50 percent for an FHA loan, you might not want to do so.
7. Mortgage Insurance Premiums
Another major difference between an FHA loan and a VA loan is the mortgage insurance premium requirement. FHA loans require you to pay both an upfront mortgage insurance premium and a monthly premium. Unless your down payment is 10 percent or higher, you’ll need to pay the monthly premium for the entire term of the loan.
In contrast, VA loans don’t have mortgage insurance. They do have a one-time funding fee, which you pay upfront. The funding fee ranges from 1.4 to 2.3 percent and is based on the size of your down payment.
8. Interest Rates and Closing Costs
VA loans tend to have lower interest rates than conventional mortgages or FHA loans. Additionally, the closing costs on VA loans tend to be lower than for other types of mortgages. While VA loans have fixed interest rates, FHA loans can have fixed or adjustable interest rates.
9. Loan Length
One thing VA and FHA loans have in common is that both are available in a range of terms. Depending on your budget and needs, you can apply for a 30-year FHA loan or a 30-year VA loan. The mortgages are also available in 15-year or 10-year terms.
10. Application Process
Both VA and FHA loans require you to apply and to submit documentation and paperwork to verify your identity and income. You can expect to submit paystubs, income tax returns, bank statements and proof of other debts when you apply. Requirements can vary from lender to lender.
[download_section]
FHA vs. VA Home Loan: Which Is the Right Loan for You?
Since VA loans are only available to qualified veterans or active-duty service members, if you don’t have a history of service in the armed forces, you most likely don’t qualify for a VA loan. But even if you are a veteran or active-duty service member, you might still be wondering whether an FHA or VA loan is better for you.
One thing to consider before you apply for either is how much you can afford to put down. If you don’t have much saved for a down payment, or any money saved up, a VA loan might be the better choice. A VA loan can also be less expensive in the long run, as it doesn’t require mortgage insurance, and the closing costs and interest rates are often lower, compared to FHA or other loan options.
Your credit is another thing to consider when deciding between an FHA or a VA loan. While VA loans don’t have specific credit requirements, a lender might expect a person applying for a VA loan to have a good credit score. If your score is lower than 580, the FHA loan program might be a better choice, provided you have at least 10 percent saved for a down payment.
Find out If You Qualify for a VA or FHA Loan Today
Ready to jump in and get started with the process of finding the right mortgage for you?
Learn more about what you need to get started today.
Sources:
- https://www.hud.gov/buying/loans
- https://www.consumerfinance.gov/owning-a-home/loan-options/fha-loans/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fhaloan.asp
- https://www.hud.gov/sites/documents/17-07ML.PDF
- https://www.bankrate.com/mortgages/what-is-an-fha-loan/
- https://www.nerdwallet.com/article/mortgages/fha-loan
- https://www.benefits.va.gov/BENEFITS/factsheets/homeloans/VA_Guaranteed_Home_Loans.pdf
- https://www.va.gov/housing-assistance/home-loans/eligibility/
- https://www.hud.gov/sites/documents/4155-1_4_SECA.PDF
- https://assurancemortgage.com/first-time-home-buyer-loans/
- https://www.benefits.va.gov/WARMS/docs/admin26/pamphlet/pam26_7/ch04.pdf
- https://www.hud.gov/program_offices/housing/sfh/lender/origination/mortgage_limits
- https://www.va.gov/housing-assistance/home-loans/loan-limits/
- https://entp.hud.gov/idapp/html/hicost1.cfm
- https://www.va.gov/housing-assistance/home-loans/loan-types/purchase-loan/
- https://www.benefits.va.gov/WARMS/docs/admin26/pamphlet/pam26_7/ch04.pdf
- https://www.military.com/money/home-ownership/how-fha-and-va-loans-stack-up.html
- https://www.hud.gov/answers
- https://www.nerdwallet.com/blog/mortgages/fha-vs-va-loan/
- https://www.consumerfinance.gov/ask-cfpb/what-is-a-debt-to-income-ratio-why-is-the-43-debt-to-income-ratio-important-en-1791/
- https://www.hud.gov/sites/dfiles/SFH/documents/SFH_FHA_INFO_19-07.pdf
- https://www.hud.gov/sites/documents/17-07ML.PDF
- https://www.va.gov/housing-assistance/home-loans/funding-fee-and-closing-costs/
- https://www.hud.gov/program_offices/housing/sfh/ins/203armt
- https://assurancemortgage.com/apply/
- https://www.military.com/money/home-ownership/how-fha-and-va-loans-stack-up.html
No, it’s not just you. Understanding conventional versus federal housing administration (FHA) loans can feel like learning another language. Throw in terms like private mortgage insurance, debt-to-income ratios, interest accrual and insurance premiums and suddenly you feel like calling to give Fannie and Freddie a piece of your mind.
Understanding these two home mortgage options is key to making an informed decision. Let’s break down the ins and outs of conventional versus FHA loans so you can feel empowered in choosing the right loan for your financial health.
- What Are FHA Loans?
- What Are FHA Loan Requirements?
- Other Questions to Consider Before Getting an FHA Loan
- Are There Any Purchasing Restrictions or Limitations on FHA Loans?
- Who Is an FHA Loan Best For?
- Who Should Not Get an FHA Loan?
- What Is a Conventional Loan?
- Conventional Mortgage Requirements
- How Do Purchasing Restrictions and Limitations Compare to FHA Loans?
- Other Questions to Consider Before Getting a Conventional Mortgage
- Comparing FHA Versus Conventional Loans Limitations
- Comparing Credit Score Requirements for FHA Versus Conventional Loans
- Are Down Payments Different for Conventional Loans Versus FHA Loans?
- How to Choose the Right Mortgage for You
What Are FHA Loans?
Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans are home mortgages insured by the federal government. Generally speaking, it’s a mortgage type allowing those with lower credit scores, smaller down payments and modest incomes to still qualify for loans. For this reason, FHA loans tend to be popular with first-time homebuyers.
The goal of FHA mortgages is to broaden access to homeownership for the American public. While FHA loans are insured by the federal agency with which it shares its name, you still work with an FHA-approved private lender to procure this mortgage type.
What Are FHA Loan Requirements?
Every year, the Federal Housing Administration, along with a slew of assisting government agencies, publishes their 1,000-plus-page FHA loan handbook.
If federal loan manuals (or should we say manifestos) don’t make your reading list cut, no problem. We’ve summed up the top FHA loan requirements applicable to today’s prospective home buyers:
- Mandatory FHA mortgage insurance: Borrowers with FHA loans must also pay FHA mortgage insurance. With conventional loans, mortgage insurance is optional and only mandatory when your down payment is less than 20 percent of the home’s value. However, this rule is less of a “gotcha” tactic and more of a market stabilizer, since FHA mortgage insurance covers your lender if you end up defaulting on your loan.
- Mandatory minimum down payments: FHA loan qualifiers pay down payments partially dictated by credit score. Credit scores on the lower end of the spectrum typically require a 10 percent down payment. Mid-range to high credit scores typically are able to put down around 3.5 percent.
- Debt-to-income (DTI) ratio: DTIs calculate the amount of money you spend every month on outstanding debts compared to your total income. To secure an FHA loan, qualifiers typically have a DTI of 30 to 50 percent. Generally, the lower the DTI, the more competitive the borrower.
- Primary residency: All properties a buyer intends to use their FHA loan on must be considered their primary place of residence, not a vacation or rental property.
- Verifiable employment, income: Like most loan types, you must provide a minimum of two years of employment history or verifiable income to qualify for an FHA loan. (Think pay stubs, federal tax returns or bank statements to name a few.)
Note: FHA’s mandatory mortgage insurance requires borrowers to pay not one but two mortgage insurance premiums: Upfront premiums and annual premiums.
- Upfront mortgage insurance premium: Currently, upfront insurance premiums for FHA loans are a small percentage of the total loan amount. It is paid as soon as the borrower receives their loan.
- Annual mortgage insurance premium: Like upfront mortgage insurance premiums, annual mortgage insurance premiums are calculated based off of a small percentage of the total loan amount.However, variables like loan terms (15 or 30 years) also influence rates. This premium is paid monthly, with installments calculated by taking the premium rate and dividing it by 12 months.
Other Questions to Consider Before Getting an FHA Loan
FHA loans are designed to be a more generous pathway to homeownership. Its underwriting standards are geared toward buyers who may not have traditionally lender-attractive credit scores or incomes but can still prove limited liability.
With that said, there are a handful of questions to ask before securing an FHA mortgage.
1. Are There Any Purchasing Restrictions or Limitations on FHA Loans?
Yes. Your FHA loan terms will maintain the following stipulations:
- Loan amounts: FHA loan amounts are dictated by a county’s median home price. While some exceptions exist, your qualifying FHA loan amount will fall near that median county value, known as its floor or ceiling amount. Also note: For the majority of U.S. home markets, FHA loans have limits on the cost of the home purchased — making a home outside this price range generally unattainable.
- Fixed interest rates: FHA loans only carry fixed, not variable, interest rates.
- Premiums: Remember those two types of FHA mortgage insurance premiums described earlier? Annual premiums can be refinanced, but only by turning the loan into a non-FHA mortgage or after you sell your home.
2. Who Is an FHA Loan Best For?
Since FHA mortgages are easier to qualify for, they’re particularly attractive for individuals in the following circumstances:
- Young or first-time homebuyers: Over 80 percent of all FHA loans lent in the past two years have been to first-time homeowners.
- Househunters with smaller savings: FHA loans statistically court lower down payments. Buyers with less competitive down payment capabilities may find FHA terms more favorable.
- Househunters with modest or variable income: The lower interest rates on most FHA loans can provide breathing room for buyers with tighter budgets or variable income, including freelancers or those who are self-employed.
3. Who Should Not Get an FHA Loan?
Borrowers turned off by the loan limit may find FHA mortgages too restrictive.
Likewise, most lenders recommend your monthly mortgage payments should not exceed 31 percent of your gross monthly income. Some private lenders offering FHA loans may allow up to 40 percent. If either of those rates proves to siphon too much of your monthly income, an FHA loan still may not be right for you.
FHA Loan Benefits
FHA loans carry several unique advantages.
1. Thoroughness of Property Appraisals
Property appraisals for FHA loans are extensive. Compared to conventional loan property assessments, inspectors will conduct a detailed analysis of the safety, structural integrity, design, HUD property guideline alignment and true value of your desired home, as well as compliance with local ordinances and standards.
2. Easier Approval
FHA-approval standards involve lower credit scores and more forgiving debt-to-income ratio allowances. Data from the Department of Housing and Urban Development show that a significant portion of FHA qualifiers maintain average credit scores or above.
3. Fixed Interest Rates
When it comes to fixed versus variable interest rates, one isn’t necessarily superior to the other. Depending on your financial situation and general risk tolerance, though, the fixed interest rates of most FHA loans may provide more budget stability than fluctuating ones.
4. Closing Costs
FHA loans typically have lower closing costs due to restrictions on the amount the lender can charge. This restriction works as a cost control for new home buyers.
What Is a Conventional Loan?
Conventional loans are mortgages issued through private lending institutions, such as banks and mortgage lenders.
Unlike FHAs, conventional loans are not insured by the federal government. They also can have fixed or variable interest rates, higher qualifying credit scores and more competitive down payment amounts affecting those interest rates.
Conventional Mortgage Requirements
Borrowers considering conventional loans have stricter qualifications to meet private lender requirements. Some of these qualifications include:
- Private mortgage insurance: If a borrower provides a down payment of less than 20 percent, then they must additionally purchase mortgage insurance paid in monthly installments. However, down payments higher than 20 percent do not require private mortgage insurance.
- Credit scores: Most private lenders require a minimum credit score to be an attractive loan candidate.
- Debt-to-income ratio: Conventional lenders look favorably on lower DTIs. Conventional loan DTIs are also capped at a moderate or mid-range credit score, though exceptions exist for those with credit scores higher than 700, though exceptions may exist for borrowers with very high or even perfect credit.
- Verifiable employment, income: Like FHA loans, borrowers must provide proof of steady income and employment to qualify for a conventional mortgage. After-tax income requirements may be higher as well, depending on the lending institution.
How Do Purchasing Restrictions and Limitations Compare to FHA Loans?
Generally speaking, conventional mortgages carry more restrictions than their FHA counterparts. Private mortgages tend to require:
- Higher credit scores
- Higher monthly income
- Higher down payment amounts, namely to access lower interest rates
It’s important to remember that one mortgage type is not better than the other. Rather, FHA and conventional loans fit particular situations that are always best reviewed with a local loan officer.
Other Questions to Consider Before Getting a Conventional Mortgage
Conventional mortgages do involve several unique processes, both before qualifying and after you’ve been approved. Consider the following questions if weighing a conventional loan against an FHA mortgage.
1. Who Is a Conventional Loan Best For?
Conventional loans work best for people in the following circumstances:
- People with high credit scores: If your credit score is 640 or above, conventional loans are advantageous.
- People house-hunting for vacation or rental properties: Conventional loans can be used on secondary properties or homes the owner does not occupy.
- People with a 20 percent down payment: Generally, putting down at least 20 percent lets you avoid private mortgage insurance — and the thousands of dollars PMI can cost over the course of your loan.
2. Who Should Not Go With a Conventional Loan?
Prospective homeowners with variable income or low debt-to-income ratios tend to have a harder time securing a conventional loan with favorable terms. Low debt-to-income ratios — meaning your monthly debt payments eat a larger portion of your income — make it particularly difficult to present as an attractive borrower to private lending institutions.
Conventional Loan Benefits
Borrowers who qualify for conventional mortgages experience several advantages:
1. No Upfront PMI, Optional Annual PMI
Conventional loans do not require upfront mortgage insurance. What’s more, annual PMI is not typically required if you meet the minimum down payment requirements, and in most situations PMI falls off your loan once you have paid off a certain percentage of the loan.
2. Flexible Loan Terms
Not only are conventional loans granted in higher values, but they come in more flexible timelines, too. Homebuyers can negotiate 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30-year conventional loans. Plus, any private mortgage insurance the buyer did take cancels once the loan’s total value (LTV) is 78 percent or less of the current value of the property.
3. Higher Loan Values
Private, conventional loans have higher ceilings than FHA loans. Mortgages backed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac can be secured a single-family home and reach up to higher amounts in higher housing markets.
Comparing FHA Versus Conventional Loans Limitations
There are a few major takeaways when comparing conventional loans versus FHA loans’ uses and restrictions.
- Owner Occupation: Conventional loans do not require the borrower to live in the property. FHA mortgages do.
- Refinancing: Refinancing is available for both FHA and conventional loans. However, conventional loans’ refinancing is more detailed, requiring a credit check, home reappraisal, income verification and more.
- High-cost and low-cost areas affecting loan values: Both FHA and conventional mortgages have loan floors and ceilings, i.e., the minimum and maximum values you can receive. FHA loans are determined by the median home value in a county. Conventional loans vary by county, state and lender but will generally follow Fannie Mae and Freddy Mac protection standards.
- Debt-to-income ratios: The lower your debt-to-income ratio (a.k.a. the closer the two numbers), the harder it will be to secure a conventional loan. Conventional loans typically accept DTIs in the 30-43 percent range; FHA mortgages can go up to 50 percent.
Comparing Credit Score Requirements for FHA Versus Conventional Loans
Credit scores are instrumental when determining loan eligibility for both types of mortgages.
- FHA loans generally accept modest credit scores: Borrowers with lower credit scores or credit challenges are frequently approved.
- Conventional loans generally favor higher credit scores: Borrowers tend to need moderate to high credit scores to receive opportune loan terms and rates.
Do remember, though, that for both types of mortgages, the lower your credit score, the higher your interest rates will be.
Are Down Payments Different for Conventional Loans Versus FHA Loans?
Yes. Conventional loans allow down payments of anywhere from 3-20 percent, with those above 20 percent receiving more favorable interest rates and no mortgage insurance.
FHA loans allow lower down payments for borrowers who meet credit requirements
How to Choose the Right Mortgage for You
There is no single “best” type of mortgage. Instead, prospective homebuyers should review their complete finance portrait to get an accurate representation of their homeownership maturity, then begin determining loan type from there.
- Know your credit score: Don’t beat yourself up if the number you discover isn’t where you want it to be. There are plenty of ways to raise your credit score and open the doors to more competitive mortgaging options.
- Be realistic about your down and monthly payment capabilities: Whether you rent or own, the budgeting golden rule is that your housing costs shouldn’t exceed 30 percent of your income. As you home shop, be realistic about what you can genuinely afford to spend on monthly mortgage payments as well as that initial down payment. Make calculations and set an actionable budget. This is one of the most important steps to take not only when house hunting but also when choosing a loan type for that home.
- Do your housing market research: FHA and conventional loan values are tied to their immediate markets. Familiarize yourself with the pricing structures and values of neighborhoods you’re considering before contacting a loan agent.
- Calculate the total cost of ownership: Consider the “hidden” costs associated with the mortgage and homebuying process, including insurance, fees, closing costs and mandatory premium payments. When tallied, these add considerably to your total monthly housing expenditures. It can also mean the loan offer with the lower interest rate might not be the savviest option in the long term.
- Consider consulting a mortgage broker or loan officers: These are individuals who have made a career navigating the complexities of the mortgage world. If you have questions, they’ll have answers.
The Bottom Line?
Buying a home is one of life’s greatest achievements — but for many, it’s also one of its most daunting.
Don’t be intimidated! Choosing between an FHA or conventional loan is a significant process but one with many options for guidance and assistance.
If you’re looking into getting a mortgage, reach out. Assurance Financial supports online applications for both FHA and conventional loans and has loan officers on staff who are ready to walk you through every step of the process.
Popular Loan Types
- First Time Home Buyer Loans
- FHA Loans
- Conventional Loans
- Construction Loans
- VA Loans
- Jumbo Loans
- Refinancing
Additional Resources You May Also Like
When we think of mortgages, we generally assume this loan is for buying or building a new home, but a mortgage can also be used to renovate, repair or restore a home. Regardless of your situation, there is a loan out there that is right for you.
So how do you choose the right mortgage for you? What exactly are the different loan types? To find the right mortgage loan for your situation, you should understand all of your options to be sure you’re getting the ideal loan for you. If you’re looking for an explanation of the different types of mortgage loans, we’re here to help.
Table of Contents
- Different Types of Mortgage Loans Explained
- FHA
- USDA
- Construction
- VA
- Jumbo
- Conventional
- Fixed-Rate
- Adjustable-Rate
- Reverse
- Balloon
- Second Mortgages
- Finance With Assurance Financials
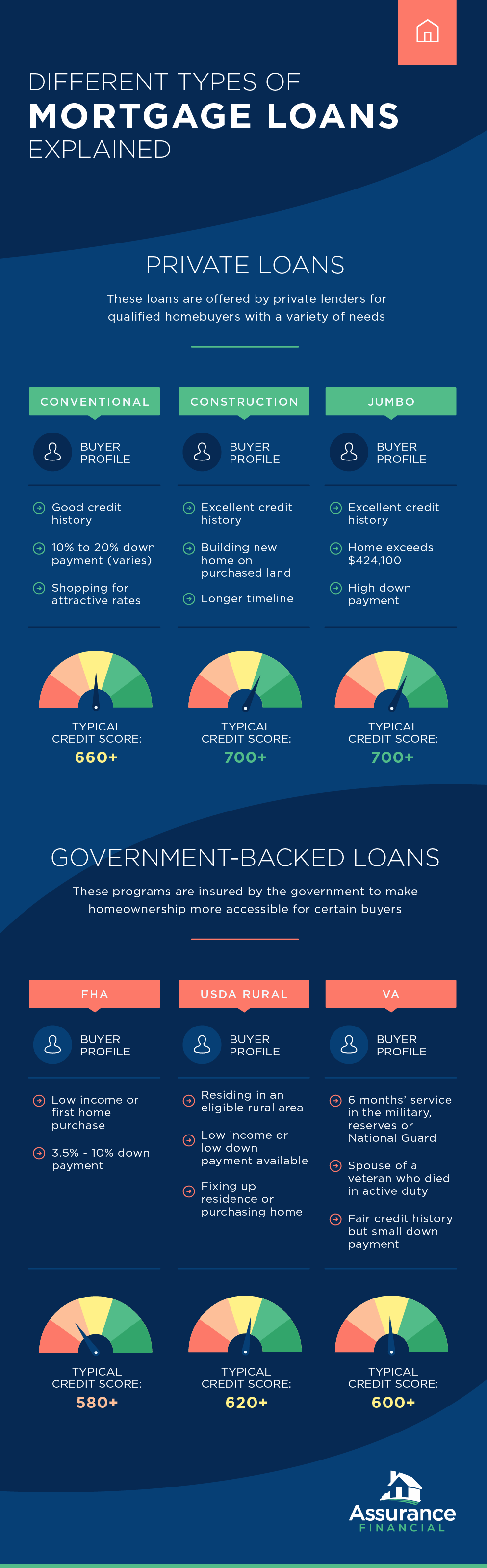
Different Types of Mortgage Loans Explained
In real estate, there are several types of mortgage loans and interest rates. Consider the following mortgages and interest rates to determine what options might be the best for you:
1. FHA
The first kind of loan we’ll discuss is the FHA loan.
What Is an FHA Mortgage Loan?
FHA stands for Federal Housing Administration. These mortgages are backed by the government and insured by the FHA.
Who Should Apply for an FHA Loan?
FHA mortgage loans are a common option for those with less-than-excellent credit and low income. They are also popular with borrowers buying their first home. Borrowers who want a fixed-rate mortgage can get an FHA loan with a fixed rate of 15 or 30 years. Repeat buyers can also get an FHA loan, provided they use the loan for purchasing a primary residence.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving an FHA Loan?
FHA requires a lower minimum credit score and down payment than other mortgage loan types. However, borrowers of an FHA loan must pay FHA mortgage insurance to protect the lender if they default on their loan. Though most borrowers must pay mortgage insurance when they put less than 20% down, all borrowers of FHA loans must pay two types of insurance premiums — an annual premium and an upfront premium.
- Annual insurance premium: Depending on the loan term, loan amount and the loan-to-value ratio, this mortgage insurance premium can range from 0.45% up to 1.05% of the total loan amount. The amount of this premium is divided by 12 for every month of the year and paid each month.
- Upfront insurance premium: This premium is 1.75% of the total loan amount and is paid once the borrower acquires their loan. The amount of the premium can be included in the financed mortgage loan amount.
Are you eligible for an FHA loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you:
- You have a FICO credit score in the range of 500 to 579 with a down payment of at least 10%.
- You have a FICO credit score of at least 580 with a down payment of at least 3.5%.
- You’ve been employed for the past two years.
- You can verify your income with pay stubs, bank statements and tax returns.
- Your FHA loan will be used for your primary residence.
- Your property is appraised and meets property guidelines.
- Your monthly mortgage payments won’t be more than 31% of your monthly income. Some lenders may allow up to 40%.
What Is the Approval Process for an FHA Loan?
The application process is intentionally designed to be flexible to increase the number of buyers entering the housing market. Closing costs for FHA lenders are limited to no more than 5% of the total loan amount.
2. USDA
A more uncommon type of mortgage loan is the USDA loan.
What Is a USDA Mortgage Loan?
This type of mortgage is given to someone who lives in a rural or suburban area designated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Borrowers must also live in the house the loan is for.
Who Should Apply for a USDA Loan?
Unlike many other loans where your credit and income are considered the most important factors, the most significant factor for this type of mortgage is the location of your home. Those who live in an eligible area can apply for this loan. These loans are great for applicants with low to moderate levels of income and those who are seeking a loan for home improvements.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a USDA Loan?
USDA mortgage loans generally have low interest rates with zero down payment, so the barriers for receiving this loan are relatively low. You must have a decent credit history, but an excellent credit score isn’t necessary to qualify.
Are you eligible for a USDA loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you:
- You have a relatively low income in your area. You can check the USDA’s page on income eligibility to determine whether you qualify.
- You’ll be making the home your primary residence, or for a repair loan, you occupy the home.
- You must be able to verify that you’re able and willing to meet the credit obligations.
- You must either be a U.S. citizen or meet the eligibility requirements for a noncitizen.
- You must be purchasing an eligible property.
What Is the Approval Process for a USDA Loan?
To get approved for USDA loan, you don’t need a down payment and you don’t need to be a first-time homebuyer. Additionally, the seller can contribute to your closing costs.
3. Construction
If you want to build a house, you’ll likely need a construction loan.
What Is a Construction Mortgage Loan?
This type of mortgage loan involves buying land on which to build a house. These loans typically come with much shorter terms than other loans, at a maximum term of one year. Rather than the borrower receiving the loan all at once, the lender will pay out the money as the work on the home construction progresses. Rates are also higher for this mortgage loan type than for others.
There are two types of construction loans — construction-to-permanent loans and construction-only loans.
- A construction-to-permanent loan is essentially a two-in-one mortgage loan. This is also known as a combination loan, which is a loan for two separate mortgages given to a borrower from a single lender. The construction loan is for the building of the home, and once the construction is completed, the loan is then converted to a permanent mortgage with a 15-year or 30-year term. During the construction phase, the borrower will pay only the interest of the loan. This is known as an interest-only mortgage. During the permanent mortgage, the borrower will pay both principal and interest at a fixed or variable rate. This is when payments increase significantly.
- A construction-only loan is taken out only for the construction of the house, and the borrower takes out another mortgage loan when they move in. This may be a great option for those who already have a home, but are planning to sell it after moving into the home they’re building. However, borrowers will also pay more in fees with two separate loans and risk running the chance of not being able to move into their new home if their financial situation worsens and they can no longer qualify for that second mortgage.
Who Should Apply for a Construction Loan?
Borrowers looking to buy land on which to build a home should apply for this type of loan. A construction loan can be used to cover the expenses of the work and materials, including permits, labor, framing costs and finishing costs.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a Construction Loan?
Construction mortgages are one of the most difficult to secure and thus also one of the most uncommon. This is because with other loans, in the event that the borrower defaults on their loan payments, the bank can then seize the home. In these cases, the home is collateral. However, with a construction loan, this isn’t an option, which makes the mortgage riskier for the bank.
The requirements for receiving this loan are a large down payment, a good to excellent credit score, a stable income and a low ratio of debt-to-income. You’ll also need savings for any extra expenses you encounter along the way during the construction of the home.
What Is the Approval Process for a Construction Loan?
To get approval for a construction loan, the borrower will need to submit to the lender a construction timetable with a realistic budget and detailed plans. Borrowers generally only need to make interest payments while construction is in progress. The lender typically sends someone to verify the home’s construction progress whenever the borrower requests funds.
4. VA
If you are a veteran, you might be eligible for a VA mortgage loan.
What Is a VA Mortgage Loan?
VA stands for Veterans Affairs. These mortgages are obtained through a lender but backed in part by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Though there aren’t any limits on the amount of a borrower’s loan, there are limitations on how much will be guaranteed by the VA.
These loans generally have lower rates than other mortgage loans. Borrowers can use their VA loan only for a primary residence, so they cannot be used for vacation homes or investment properties. VA loan holders are also not required to pay private mortgage insurance. Following six months of active duty, this mortgage type is provided with 100% financing.
Who Should Apply for a VA Loan?
VA mortgage loans can be given to members of the national guard, reserves, military or spouses of service members who died during active duty. These mortgage loans don’t require a down payment or excellent credit, so this can be an excellent option for those without much saved up for a down payment or without great credit.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a VA Loan?
Are you eligible for a VA loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you. You may qualify for a VA loan if:
- For 90 consecutive days, you served in active service during a time of war.
- For 181 days, you served in active service during a time of peace.
- For 6 years, you have been an active member of the Reserves or National Guard.
- You are the spouse of a service member who died during active service or from a disability related to their service.
You’ll also need to meet your lender’s requirements of credit score, debt-to-income ratio and income.
What Is the Approval Process for a VA Loan?
First, borrowers will need to apply for a Certificate of Eligibility. They can request this from the lender, apply through VA.gov or mail in their application form. After obtaining their COE, borrowers can then apply for their VA loan through their lender.
5. Jumbo
Another uncommon type of mortgage is the jumbo loan.
What Is a Jumbo Mortgage Loan?
Jumbo mortgages are based on the price of the home. Homes exceeding $424,100 fall into this mortgage bracket. Though historically, jumbo loans have carried higher interests than other mortgage loans, jumbo mortgage interest rates are now closer to the rates of other loan types.
Who Should Apply for a Jumbo Loan?
High-income earners making between $250,000 and $500,000 annually and who are looking to buy high-cost homes in a competitive local market or luxury homes are generally the borrowers who should apply for a jumbo mortgage.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a Jumbo Loan?
Jumbo loans are risky for lenders because of their large amount and lack of guarantee by the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae) or the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (Freddie Mac), so eligibility requirements of borrowers are more demanding. To qualify for a jumbo mortgage, you’ll need an excellent credit score of above 700, a large down payment and a low debt-to-income ratio, preferably close to 36%. Interest rates can be high but are also tax deductible.
What Is the Approval Process for a Jumbo Loan?
To get approved for a Jumbo loan, you’ll need to prove you have reserves of cash and provide W2 tax forms for two years and 30 days of pay stubs.
6. Conventional
The most common type of mortgage is the conventional loan.
What Is a Conventional Mortgage Loan?
Finally, the most common mortgage type is the conventional mortgage, representing about two-thirds of loans issued to homeowners in the US. This loan is essentially any type of mortgage that isn’t offered by a government entity such as the FHA, VA or USDA Rural Housing Service. Instead, this type of loan is available through Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. The down payment tends to be a bit higher than other mortgages, and it also offers two interest rate options — fixed and adjustable.
Who Should Apply for a Conventional Loan?
Conventional mortgages can be a great option for both new homebuyers and existing homeowners. Though interest rates tend to be higher than for government-backed loans, insurance premiums required by other loan types may result in the same total cost over the long term.
This mortgage loan type is also generally the best loan option for those who want to buy a second home, a home to use as an investment property or a home valued over $500,000.
What Are the Requirements for Receiving a Conventional Loan?
Are you eligible for a conventional loan? Review these requirements to determine whether you qualify for this mortgage loan type and whether it’s right for you:
- Your credit score is at least 680. A higher score can potentially result in a lower interest rate, especially for those with a score over 740.
- You have a reasonable or low debt-to-income ratio. The ratio of your financial obligations to your monthly income should be around 36% and should not exceed 43%.
- You have saved up enough for a down payment of 20%. Though a smaller percentage can be accepted, borrowers usually are then required to pay for private mortgage insurance.
What Is the Approval Process for a Conventional Loan?
To get approved for a conventional mortgage loan, borrowers need to complete an official application and supply their lender with any necessary documents for the lender to check their background, credit score and credit history. Lenders look for borrowers who can afford their monthly mortgage payments –– payments that typically should be 28% or less of their gross income –– can afford a down payment and can afford other upfront expenses, such as fees and closing costs.
7. Fixed-Rate
Fixed-rate mortgages come with a rate that doesn’t change during the loan’s duration. Though the amount of the principal and interest that are paid every month varies, the monthly payment stays consistent, making budgeting easier and more predictable for homeowners.
A fixed-rate mortgage protects homeowners from increases in interest rates in the housing market, but they can also be higher in comparison to variable rates. This rate can be possible for multiple term options, such as 30, 20 or 15 years.
8. Adjustable-Rate
The opposite of fixed-rate mortgages are adjustable-rate mortgages, which have variable rates. This means the rate of the mortgage can vary from year to year and are generally more complicated than mortgages with fixed rates.
The rate adjusts on an established set of time, generally every one, three or five years. If your adjustment occurs every five years, this means your monthly payments will be consistent for the first five years of your loan. After those five years, your interest rate will adjust and your payments will either increase or decrease.
9. Reverse
A reverse mortgage is a loan for a homeowner 62 years of age or older who wants to borrow against their home’s value. The homeowner doesn’t have to make loan payments, and they’ll receive their loan in the form of a lump sum, line of credit or monthly payment. The loan balance will become due when the borrower permanently moves away, sells their home or dies. The loan amount won’t exceed the value of the home, and the borrower will also not be responsible for paying more should their home’s value decrease.
These loans are an option for homeowners age 62 or older who have most of their net worth tied up in their home and need cash.
10. Balloon
A balloon mortgage is a loan in which the borrower repays in the form of a lump sum. This type of loan is typically short-term but can be held for as long as 30 years, they can have variable or fixed rates and they may require interest-only monthly payments. Balloon loans also generally offer higher interest rates due to the increased risk for lenders.
11. Second mortgages
Second mortgages are taken out after a borrower’s first mortgage and are generally used for financing home improvements, consolidating debt or for covering enough of the first mortgage to avoid the requirement of paying the mortgage insurance. Second mortgages generally have terms that last only up to 20 years and can be as short as one year.
[download_section]
Financing Your Mortgage With Assurance Financial
Financing your mortgage should be an exciting time in your life, and at Assurance Financial, we strive to help you make it a time that is as memorable and simple as possible. You should be able to enjoy this step in your journey toward homeownership while someone else handles the heavy lifting. That’s where we come in.
We’re an independent lender, and we want to make your dreams of homeownership a reality. We offer end-to-end processing all under one roof so that your path to owning your dream home is a smooth and fast one.
Find a loan officer with us today and let us help you secure the mortgage terms of your dreams for the home of your dreams.